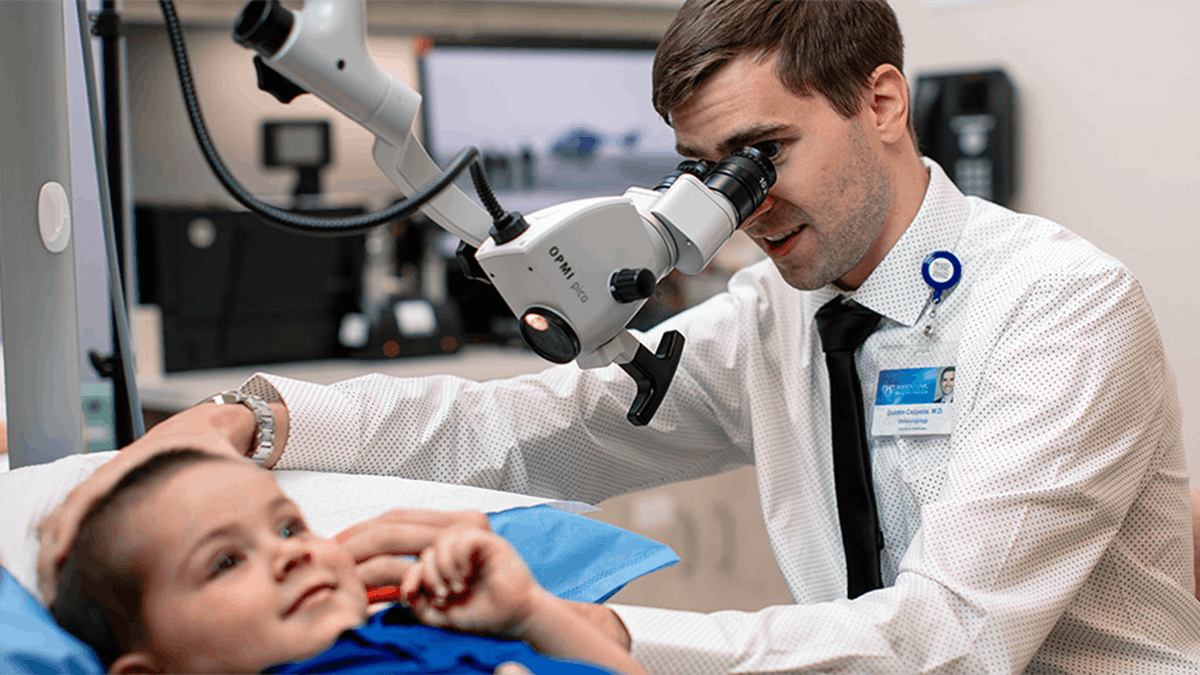
While they are usually benign, tumors that form in the inner or middle ear can cause hearing loss, balance problems and other negative effects. Tumors of the middle ear are called glomus tumors. Tumors in the inner ear are called acoustic neuromas. Large or growing tumors of the ear require surgery in order to remove them.
How are Ear Tumors Treated?
If the tumor is smaller, it may be treated with Gamma Knife radiosurgery. Gamma Knife radiosurgery is a short procedure that doesn’t require incisions. The tumor is directly addressed with radiation, but the rest of the brain is not dosed. Gamma Knife radiosurgery helps to stop or slow the growth of the tumor.
A larger tumor that is growing and affecting hearing or balance requires surgery. Gamma Knife radiosurgery may be performed after the surgery to help ensure there is no regrowth of the tumor.
Ear tumor surgery begins with general anesthesia. The tumor is carefully removed through an incision in the middle ear or through a window incision in the skull. Depending on the size of the tumor and its location, ear tumor surgery takes between 4-6 hours.