Treatments
The hearing can be restored with a surgical procedure called stapedectomy. Hearing aids can be helpful in patients who do not desire surgical treatment.
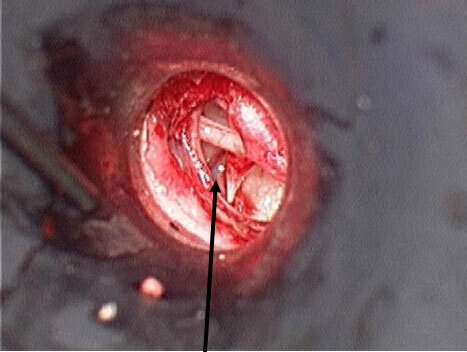
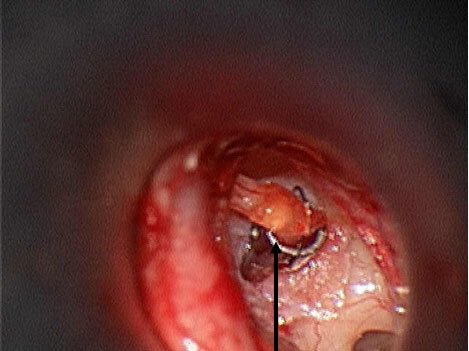
Stapedectomy
Stapes fixation due to otosclerosis or other causes can be corrected with a surgical procedure called stapedectomy. The procedure is an outpatient surgery that takes 30 to 40 minutes. It is performed under local or general anesthesia. The surgery is performed through the ear canal.